MIT experimental report: Over-reliance on AI chatbots will reduce thinking ability
Author: Excerpt from MIT
Compiled by: Felix, PANews
With the widespread adoption of large language model (LLM) products such as OpenAI's ChatGPT, companies and people from all over the world are using LLM almost every day. Like other tools, LLM also has its own advantages and limitations.
Recently, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) released a 206-page research report that explored the cognitive cost of using LLMs (such as ChatGPT) in educational contexts for writing articles, revealing the impact of using LLMs on the brain and cognitive abilities. The study showed that over-reliance on artificial intelligence chatbots such as OpenAI's ChatGPT may reduce cognitive abilities.
The research team divided the participants into three groups: LLM group, search engine group, and brain-only group. These participants used designated tools (the brain-only group did not use tools) to write articles within a limited time over a period of 4 months. The topics of the articles were different in each experiment. The team arranged 3 rounds of experiments with the same grouping for each participant. In the fourth round of experiments, the team asked the participants in the LLM group not to use any tools (called the LLM-to-brain group), while the participants in the brain-only group used LLM (the brain-to-LLM group). A total of 54 participants were recruited to participate in the first 3 rounds of experiments, of which 18 completed the fourth round of experiments.
The research team used electroencephalography (EEG) to record participants’ brain electrical activity to assess their cognitive engagement and cognitive load and gain insight into neural activation during the essay writing task. The team conducted natural language processing (NLP) analysis and interviewed each participant after each experiment. The team scored with the help of human teachers and an AI judge (a specially built AI agent).
In the natural language processing (NLP) analysis, participants who used only their brains showed a great deal of variability in how they wrote articles on most topics. In contrast, the articles written by the LLM group on each topic tended to be statistically homogeneous, with significantly less deviation than the other groups. The search engine group may have been influenced, at least in part, by the search engine promotion and optimized content.
The LLM group used the most specific named entities (NERs), such as people, names, places, years, and definitions; the search engine group used at least half as many NERs as the LLM group; and the brain-only group used 60% fewer NERs than the LLM group.
People working on the LLM and search engine groups were under additional pressure due to the limited time (20 minutes) and therefore tended to focus on the output of the tools they were using. Most of them focused on reusing the output of the tools and were busy copying and pasting instead of incorporating their own original ideas and editing them from their own perspective and experience.
In terms of neural connectivity patterns, the researchers used the dynamic directional transfer function (dDTF) method to measure participants' cognitive load. dDTF can reveal systematic and frequency-specific changes in network coherence, which is important for executive function, semantic processing, and attention regulation.
EEG analysis showed significant differences in neural connectivity patterns between the LLM, search engine, and brain-alone groups, reflecting different cognitive strategies. The degree of brain connectivity systematically decreased with increasing external support: the brain-alone group showed the strongest and most extensive network, the search engine group showed intermediate engagement, and the LLM-assisted group had the weakest overall coupling.
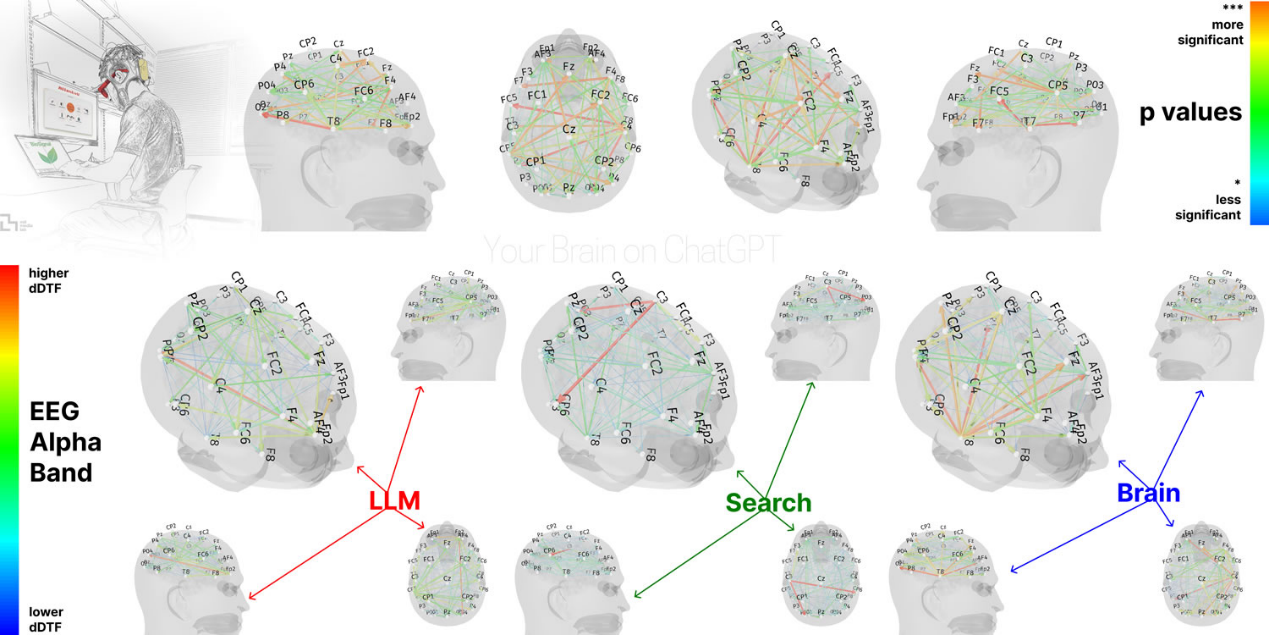
In the fourth round of the experiment, participants who went from LLM to brain-only showed weaker neural connections and lower engagement of the alpha and beta networks, while participants who went from brain-only to LLM showed improved memory recall and reactivation of widespread occipital-parietal and prefrontal nodes.
In the interviews, the LLM group had a lower sense of ownership over their articles. The search engine group had a stronger sense of ownership, but less than the brain-only group. The LLM group also lagged behind in the ability to cite an article they wrote a few minutes ago, with more than 83% of ChatGPT users unable to cite an article they wrote a few minutes ago.
The study, which has not yet been peer-reviewed, showed that participants in the LLM group performed worse on neural, language, and score levels than a control group that used only their brains over the course of the four-month study. As the educational impact of LLMs among the general public is only beginning to emerge, using AI LLMs may actually harm the improvement of learning skills, especially for younger users.
The researchers said that before LLM can be recognized as beneficial to humans, "longitudinal studies" are needed to understand the long-term effects of AI chatbots on the human brain.
When asked what ChatGPT thought of the research, it responded: “This study does not say that ChatGPT is inherently harmful – rather, it warns people not to rely too heavily on it without thought or effort.”
Related reading: a16z: From AI agents, DePIN to micropayments, 11 key implementation directions for the integration of encryption and AI
You May Also Like

Best Altcoin to Buy This Week: XRP, MATIC & MAGACOIN FINANCE Highlighted After Market Correction

FOMC and Canadian ETF Debut Fail To Pump XRP Price: What Catalyst Does XRP Need?
